- I/O errors (detected by drivers)
- Low Priority Machine Checks (LPMCs)
- System overtemps
- Logical Volume Manager (LVM) errors
- Logger events
Logging. When the logging daemon detects an event, it logs an entry in a system log file located (by default) in the directory "/var/stm/logs/os". The raw log file names have the format "logN.raw," where N is a number that starts at 1 and is incremented each time a new log file is created with the command Switch Log. The only exception to the raw log file naming convention is the log file to which the logging daemon is currently logging data; this file is called "logN.raw.cur."
Memory errors, when detected by the memory logging daemon, are logged into the memory log file called memlog.
Logging Control. To change the file to which the daemon is logging data, select the Switch Log command from the File Menu. A new current raw log file will be generated when an error is logged.
You can modify the behavior of the logging daemon by editing the configuration file "diaglogd.cfg" located in the directory "/var/stm/config/sys". The file itself contains documentation regarding its format.
Logtool and the Logging Process.
The role of Logtool in the logging process is shown in the
diagram and is explained in more detail below.
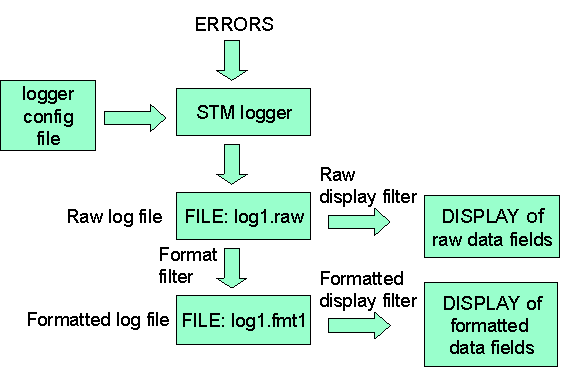
Raw Log Files. The first step in analyzing the logs is usually to enter the Select Raw command from the File Menu. A summary of the contents of a log will automatically be displayed. In addition the summary information can be obtained with the Raw Summary command in the View Menu. To view the entries in the log file, you use the Raw Log command in the View Menu.
Looking at all the entries in the raw log file can be burdensome:
- The entries in the raw log file are difficult to read.
- A log file can contain an overwhelming amount of data.
Formatting the Data. To translate the raw log file into a more readable format, select the Format Raw command from the File Menu. The formatted data is put into a file with the name "logN.fmtN" where the first number (N) matches that of the raw log file and the second number (N) starts at 1 and is incremented for each new formatted file generated from the same raw log file. If multiple files have been chosen, the file name will have a plus sign("+") in it. For example, log1.raw and log2.raw will be formatted into log1+.fmt1.
To choose a particular formatted file for viewing or filtering, use the Select Formatted command from the File Menu. A summary of the contents of the formatted log can will automatically be displayed. To view the entries in the formatted log file, you use the Formatted Log command in the View Menu.
Filtering the Data. Even if the data is formatted, there is generally a large number of entries contained in a typical log. When you are troubleshooting a problem, only certain entries may be relevant. For example, you may want to see only I/O errors that occurred during a certain time period on a certain hardware path.
Logtool offers three different filters to select the entries relevant to your task.
- To filter entries before the formatting of a raw log file, select the Format command in the Filters Menu.
- To filter entries before the viewing of a raw log file, select the Raw command in the Filters->Display Menu.
- To filter entries before the viewing of a formatted file, select the Formatted command in the Filters->Display Menu.
Memory Log. The memory log is handled somewhat differently than the system logs described above. The commands to view the memory report log or to clear the memory log are found in the Memory Menu. You can also use the Memory->Set Timer command to change the memory polling interval.
The memory report log can be viewed in two separate ways. The entire log file can be viewed (View Detail) or information pertaining only to memory deallocation can be viewed (View Dealloc).
Chassis Logs. The chassis code logging daemon logs information to the chassis code error log file and boot log files called ccbootlog and ccerrlog respectively. These log records are generated by various system hardware, software and firmware modules. They can contain error indications as well as informational messages. Chassis code logging was implemented beginning with the introduction of N-class systems on HP-UX 11.00, and will be featured on some newer systems as they are released.
Log Entry Types. The entry types currently logged by Logtool include:
- I/O Error Entry.
Logged by I/O system drivers, I/O error entries typically contain information concerning exception conditions that the driver encountered.- Entries in the raw log file have four components:
- Device Path: the hardware address of the device. For example, "2/0/1.1.0".
- Product: The type of device. For example, "SCSI Interface," "LAN Interface," "SCSI Disk."
- Product Qualifier: Additional information about the device. For example "HPC2490AM."
- Logger: The logging entity (usually a software device driver). For example: "lanmux0," "disc30," "scsi1."
- Entries in the formatted log file have two additional components:
- Device Type: The general type of device. For example, "Interface," or "Disk."
- Device Qualifier: Additional information about the device type. For example: "LAN," "SCSI," "Hard."
- Entries in the raw log file have four components:
- Low Priority Machine Check (LPMC) Entry
Logged by the system when a Low Priority Machine Check (LPMC) condition has occurred. An LPMC is a recoverable error detected by hardware; the hardware is able to recover from the error and continue operation, though perhaps in a degraded fashion. In contrast, a High Priority Machine Check is an error detected by hardware from which it cannot recover. - System Overtemp Entry
Logged by the system when hardware detects a recoverable over-temperature condition (over-temp warning). - Logical Volume Manager (LVM) Entry
Logged by the Logical Volume Manager, typically containing information concerning exception conditions the manager encountered. - Logger Entry
Logged by the logger process. The type of events that are logged include suspension and resumption of logging.
